Research
-
Astaroth banking trojan leverages GitHub to restore command-and-control, McAfee says
McAfee Labs reported that the Astaroth banking trojan campaign uses GitHub-hosted images with steganography to update configurations and maintain access after C2 takedowns; the campaign targets Brazil and other Latin American countries and is delivered via DocuSign-themed phishing emails.
-
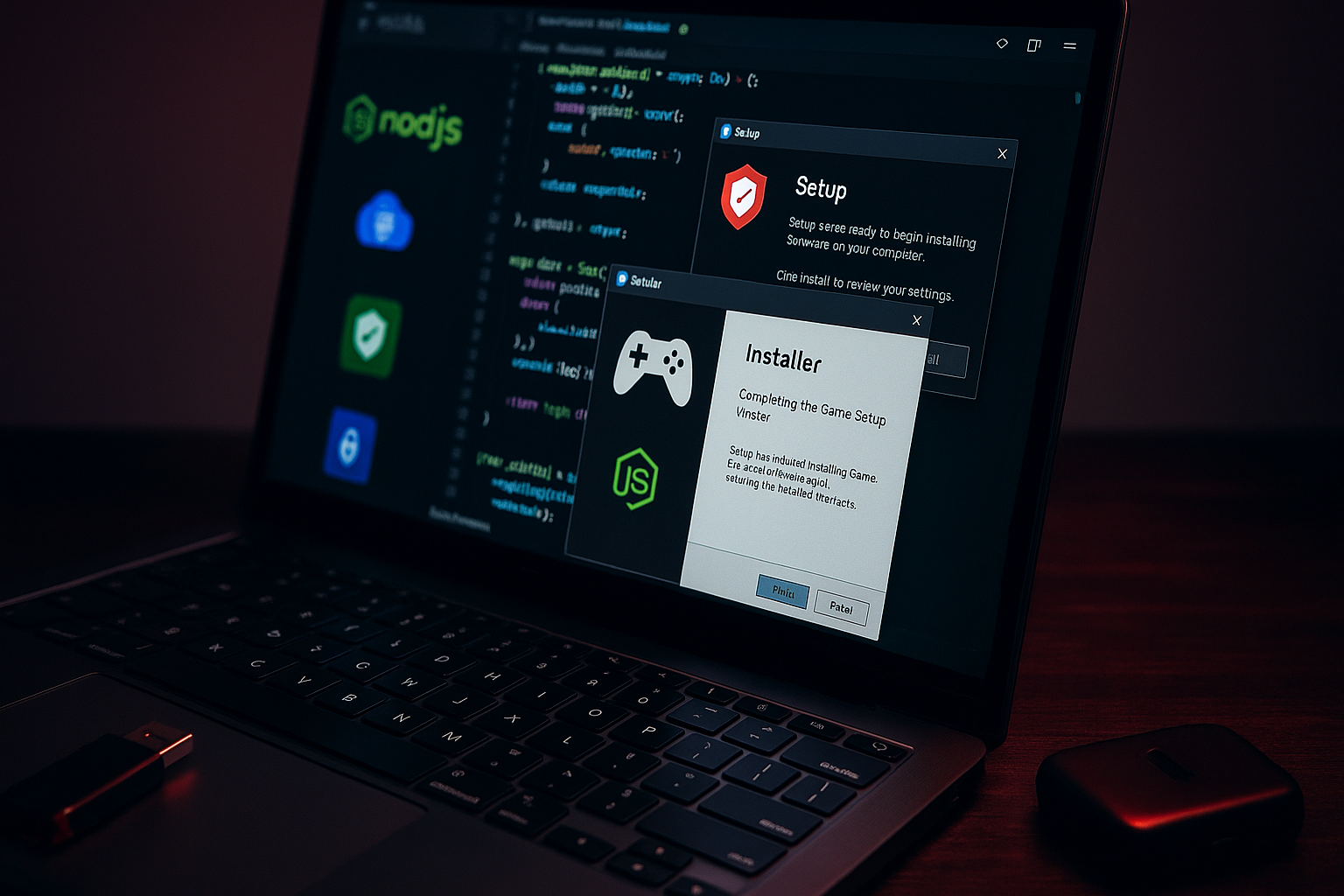
Researchers: Stealit malware uses Node.js single-executable feature to spread
Fortinet researchers said the Stealit malware campaign is abusing Node.js’ experimental Single Executable Application feature and, in some variants, Electron, to distribute stealers and a RAT via counterfeit installers on file‑sharing sites.
-
Researchers find 175 npm packages used to host phishing infrastructure in ‘Beamglea’ campaign
Researchers say 175 npm packages were used to host redirect scripts and HTML payloads for a credential-phishing campaign called Beamglea that has been downloaded about 26,000 times and targeted more than 135 companies worldwide.
-
New FileFix Variant Uses Cache Smuggling to Evade Security, Researchers Say
A new FileFix phishing variant uses cache smuggling to store a malicious ZIP in browser cache and run it via a hidden PowerShell command, letting it evade many security products, researchers said.
-
Crimson Collective targets AWS cloud instances to steal data and extort firms
Researchers at Rapid7 said the Crimson Collective has been exploiting exposed AWS credentials to create privileged IAM users, export database and storage snapshots for exfiltration, and issue extortion demands; AWS recommended using short‑term, least‑privileged credentials and provided remediation guidance.
-
Patched command injection in Figma MCP server could allow remote code execution, researchers say
A command injection bug in the figma-developer-mcp Model Context Protocol server, tracked as CVE-2025-53967 and scored 7.5, could allow remote code execution by interpolating unvalidated input into shell commands; the issue was fixed in version 0.6.3 and researchers recommend avoiding child_process.exec with untrusted data.
-
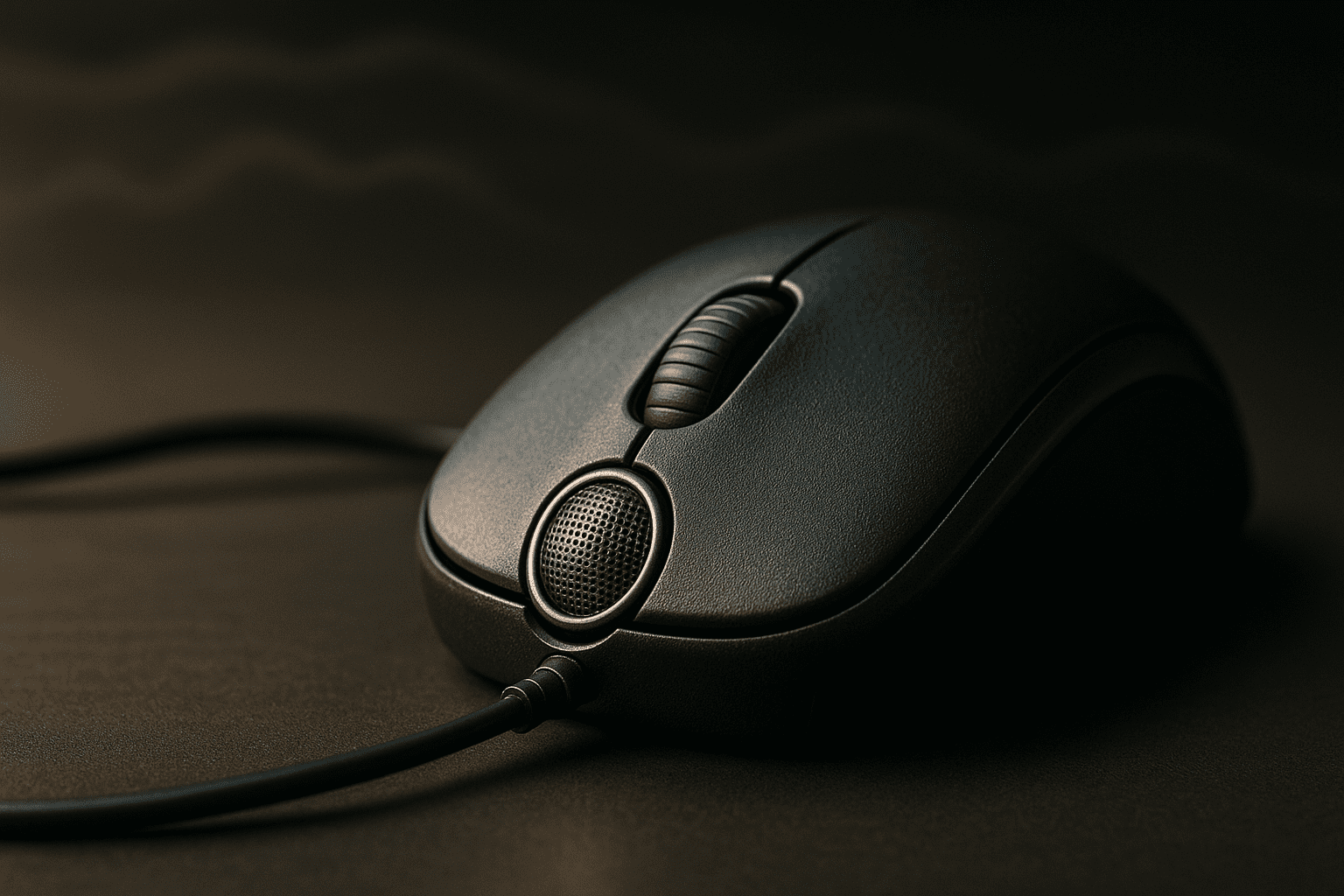
UC Irvine researchers say high-precision mice can be used to eavesdrop on conversations
Researchers at the University of California, Irvine say high-precision optical mice can pick up tiny desk vibrations from speech and, using signal processing and machine learning, be converted into audible reconstructions; the team published details on a Google research site and an arXiv paper.
-
Google DeepMind unveils CodeMender to detect, patch and rewrite vulnerable code
DeepMind has unveiled CodeMender, an AI agent that detects, patches and rewrites vulnerable code using Gemini models and an LLM-based critique tool; Google says it has upstreamed 72 fixes and is expanding AI security measures including an AI Vulnerability Reward Program and updates to its Secure AI Framework.
-
Google launches AI Vulnerability Reward Program with bounties up to $30,000
Google this week launched an AI Vulnerability Reward Program offering up to $30,000 for high-quality reports on flaws in its AI products, covering Search, Gemini, Workspace and other AI systems and laying out tiered payouts for issues such as rogue actions and data exfiltration.
-
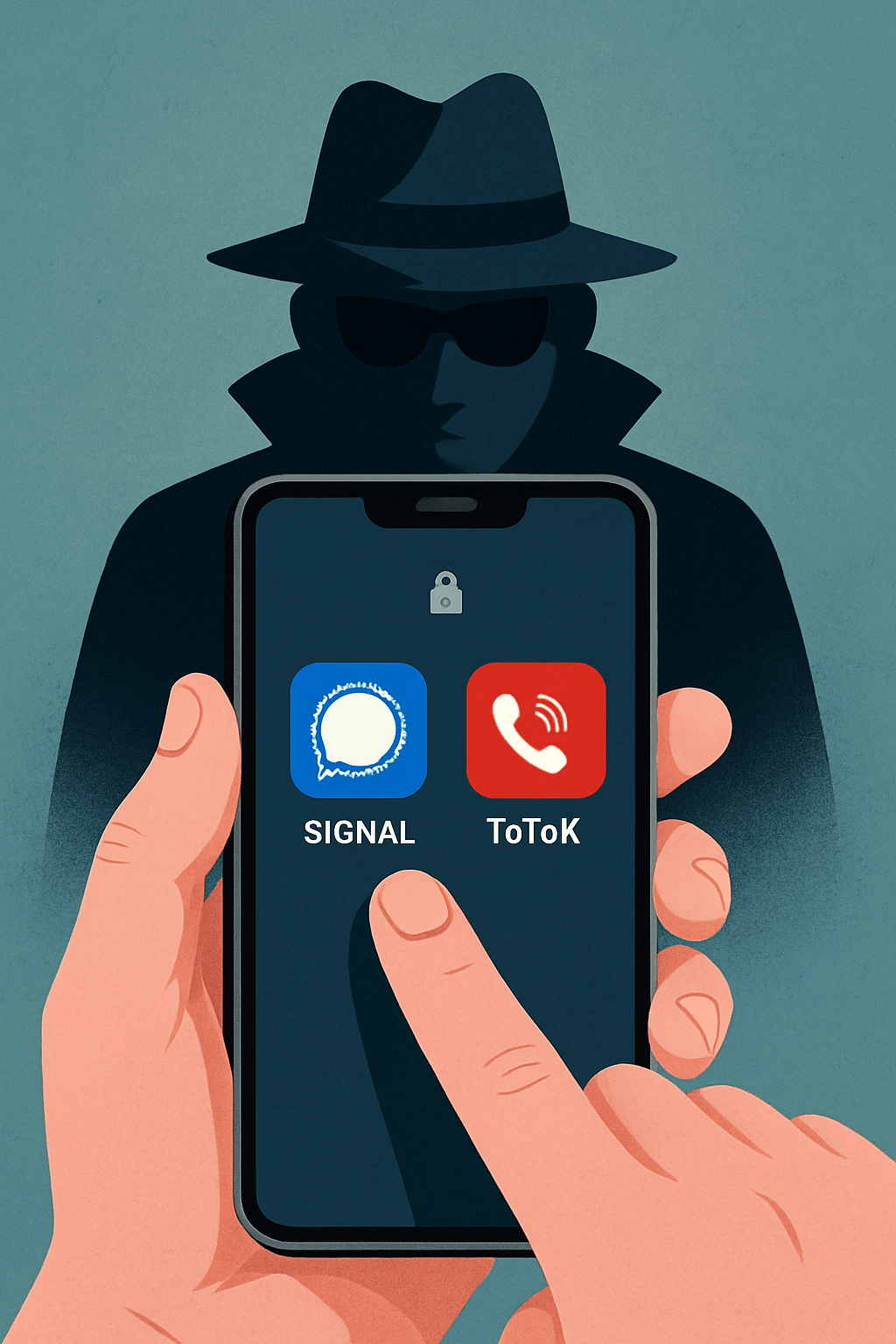
ESET: Fake Signal and ToTok Android Apps used to deploy spyware in UAE
ESET researchers warned that two spyware campaigns in the UAE use fake Signal and ToTok Android apps disguised as plugins or add‑ons to collect contacts, messages, backups and files; the spyware has been traced to mid‑2022 and is blocked by Google Play Protect for devices with Google Play Services.